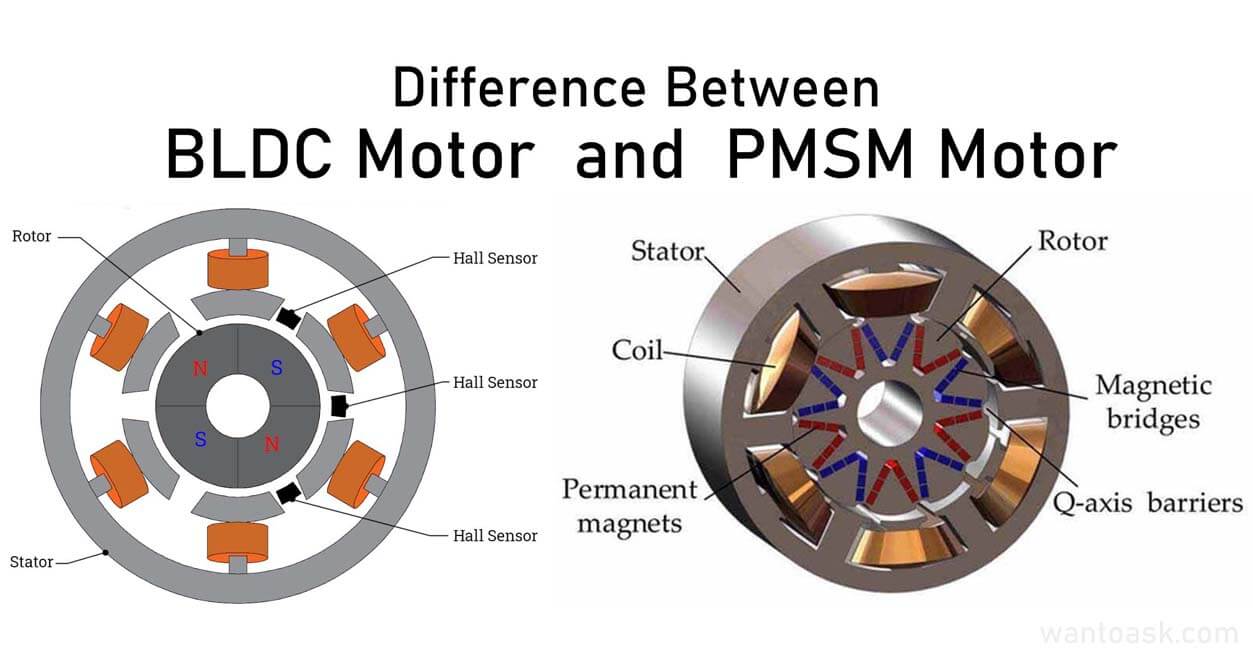
What Is the Difference Between BLDC and PMSM Motors?
BLDC (Brushless DC Motor) and PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor) are two of the most widely used modern electric motors today. They are popular because they offer high efficiency, low maintenance, and compact size.
Although both motors look similar in construction and both use permanent magnets, their operating principles, control methods, and performance characteristics are different.
Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right motor for applications like electric vehicles, home appliances, industrial automation, and robotics.
What Is a BLDC Motor?
A BLDC motor (Brushless DC Motor) is a motor that does not use mechanical brushes for commutation.
Despite the name “DC,” a BLDC motor does not behave like a traditional brushed DC motor internally.
Key Concept (Very Important)
The motor is powered by a DC supply
But the stator windings are energized with alternating current
Commutation is done electronically, not mechanically
This is why BLDC motors are sometimes described as “electronically commutated AC motors powered by DC.”
How a BLDC Motor Works
The rotor contains permanent magnets
The stator contains windings
An electronic controller (inverter) switches current between stator phases
Rotor position is detected using Hall sensors or sensorless methods
Current is applied in a six-step (trapezoidal) pattern
Characteristics of BLDC Motors
No brushes → no sparking or mechanical wear
Trapezoidal back EMF
Trapezoidal or rectangular current waveform
Slight torque ripple due to non-sinusoidal commutation
Simple control logic compared to PMSM
Advantages of BLDC Motors
Common Applications of BLDC Motors
What Is a PMSM Motor?
A PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor) is also a brushless motor that uses permanent magnets on the rotor.
Unlike BLDC motors, PMSMs are designed to operate with purely sinusoidal waveforms.
How a PMSM Motor Works
The rotor has permanent magnets
The stator is supplied with sinusoidal AC currents
The rotor speed remains synchronous with the rotating magnetic field
Typically controlled using Field-Oriented Control (FOC)
Characteristics of PMSM Motors
Sinusoidal back EMF
Sinusoidal current waveform
Very smooth torque output
Minimal torque ripple
Higher control complexity
Advantages of PMSM Motors
Higher efficiency than BLDC, especially at low speeds
Very smooth and quiet operation
High torque density
Excellent speed and position control
Common Applications of PMSM Motors
Electric vehicles (cars, buses, two-wheelers)
Robotics
CNC machines
Elevators
Wind turbines
High-end industrial drives
Servo systems
Key Differences Between BLDC and PMSM Motors
| Feature | BLDC Motor | PMSM Motor |
|---|
| Brushes | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Power supply | DC input | DC or AC via inverter |
| Back EMF | Trapezoidal | Sinusoidal |
| Current waveform | Trapezoidal / six-step | Sinusoidal |
| Torque ripple | Higher | Very low |
| Noise & vibration | Higher | Lower |
| Control complexity | Simple | Complex (FOC) |
| Controller cost | Lower | Higher |
| Efficiency | High | Very high |
Are BLDC Motors Actually AC Motors?
Yes — electrically speaking, BLDC motors operate like AC motors.
The term “DC motor” is used because:
This naming convention often causes confusion, but it is important to understand that:
Which Motor Should You Choose?
Choose BLDC if:
You want a cost-effective solution
Simple speed control is sufficient
Minor torque ripple is acceptable
Choose PMSM if:
You need maximum efficiency
Smooth torque is critical
Precise control is required
Final Conclusion
BLDC and PMSM motors are both advanced, efficient, and brushless motor technologies.
The main difference lies in their back-EMF shape, current waveform, and control strategy.
Understanding this difference avoids common misconceptions and helps in selecting the right motor for your application.